When you create or revise the course learning outcomes (CLOs) for a course, think about the 4-9 most important things that students should learn in the course. Focus on high-level, broad framing outcomes for CLOs instead of specific, discreet things that students will learn. The CLOs should be the big-picture knowledge and skills that students should have when they successfully complete a course.
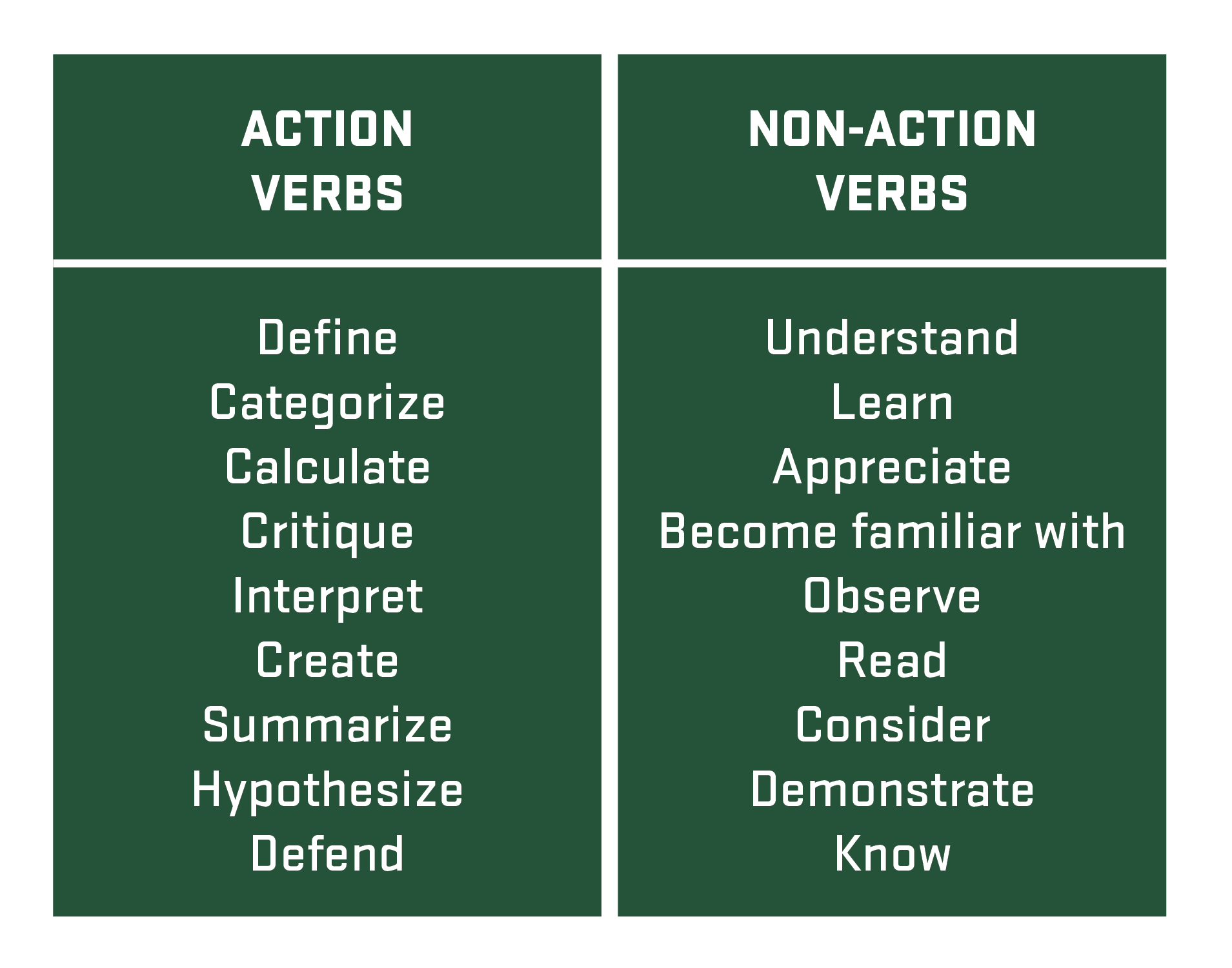
Identify verbs that are observable/measurable.
Action verbs are the most suitable type of verb to use when writing learning outcomes. Action verbs are observable and explain how the student will show their knowledge upon completion of the course.
In contrast, non-action verbs are not observable, making it difficult to accurately measure the student's new knowledge, skill, or ability.
Each CLO must only have one action verb. A statement with more than one verb is difficult to measure.
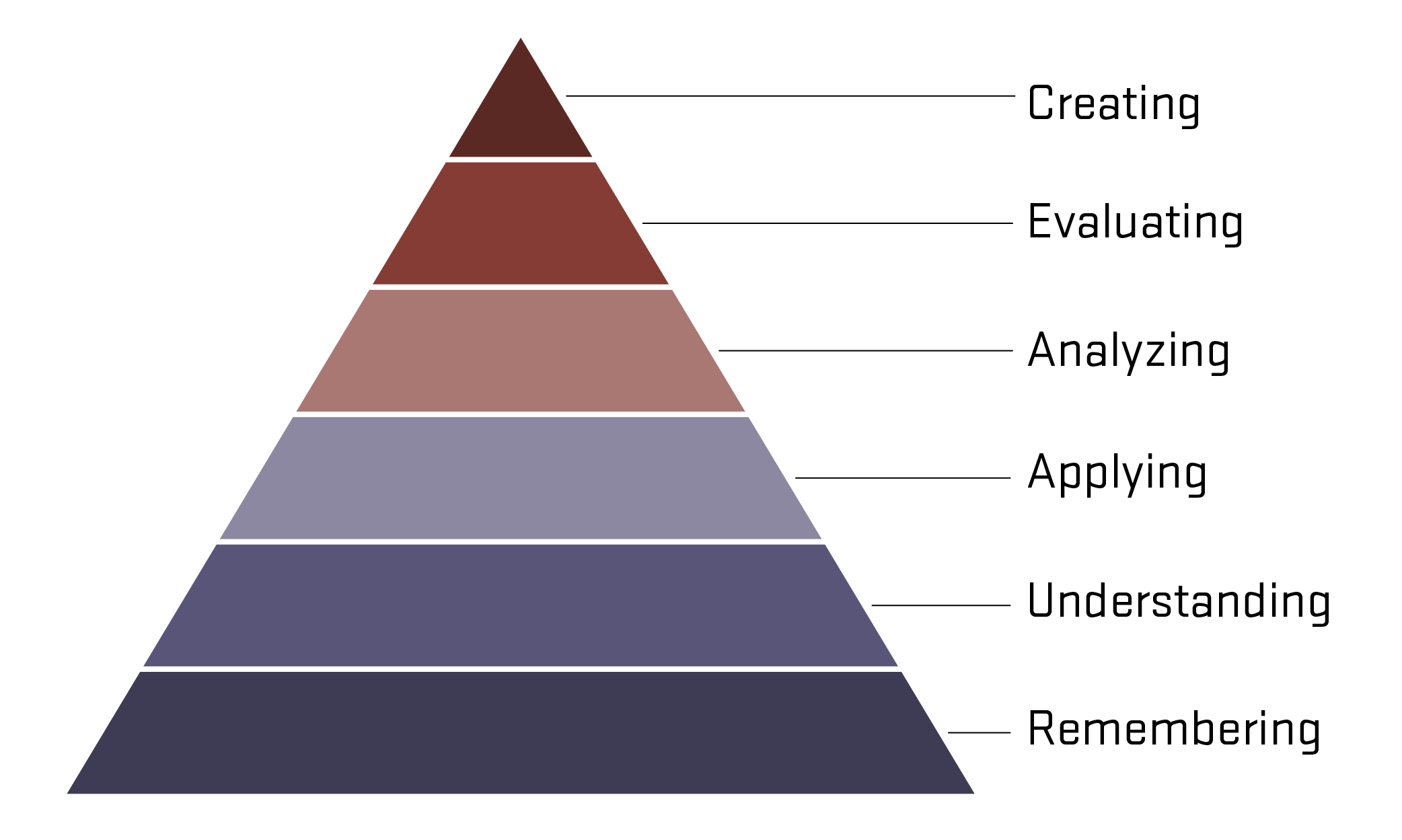
Revised Bloom's Taxonomy (2001) is a categorization of cognition levels based on Benjamin Bloom's initial Bloom's Taxonomy, published in 1956. The authors generated a list of action or measurable verbs associated with each level. Educators use these action verbs to write observable learning outcomes.
Course descriptions explain what the course does and are printed in the course catalog. The general public reads them, including students, parents, other universities, businesses, and accrediting bodies.
Examines objectives, instructional methods and curriculum for teaching science in the secondary school. Includes developing, adapting, evaluating, and using strategies and materials for teaching biological and physical sciences. Explores special needs of the learners and characteristics specific to the science discipline.
Introduces the fundraising development process, cultivating donors, and raising money through donations, sponsorships, and grants to support nonprofit arts organizations.
Provides an introduction to basic concepts, theories, principles of oral communication as applied to a variety of speaking situations. Develops competence in oral communication through performance, the development of critical thinking skills, arrangement of ideas, and use of evidence and reasoning to support claims. Explains how culture influences what is considered effective public speaking.
*Note: Fees will be placed in the catalog based on the determination of the fee committee.
For assistance in writing course outcomes, contact the Office of Teaching and Learning. For all other questions, contact the Curriculum Office.