Text formatting describes features within word processors that are used to change the appearance of the text, such as its size and color. Knowing how to format text helps to make written work look consistent and professional. Formatting can also add emphasis, style, or additional meaning to text. Most word processers allow you to format text using options in the toolbar and following similar steps.
Microsoft Word and Google Docs are two of the most common word processors. Both programs have several text-formatting features, including font type, font size, bold, italics, underline, text color, and highlight. Taking the time to correctly format a document is often part of following style and citation guidelines.
If you can’t find formatting options, they may be hidden because your window is too small to show them. Try maximizing your window or trying one of the following tricks to reveal hidden options:
![]()
In Microsoft Word (Windows), if the top toolbar is hidden, click on the “view” tab to show the toolbar. Click the pin icon in the far bottom-right of the toolbar to keep at the top of the page.
In Microsoft Word (Mac), click the “view” tab to hide or reveal the toolbar.
![]()
In Google Docs, click the three vertical dots on the right of the toolbar to see hidden tools.
There are two main ways to apply text-formatting, which are standardized across both Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
If you change a text-format setting before you type, everything you type from then on will use that format.

This is useful when you know the next words you type will need to be formatted in a specific way.
If you want to change the format of text you have already written:

Font describes the style of a text’s lettering. There are many fonts you can choose from, but most academic work will be written in Arial, Calibri, Times New Roman or another simple font.
To change font:
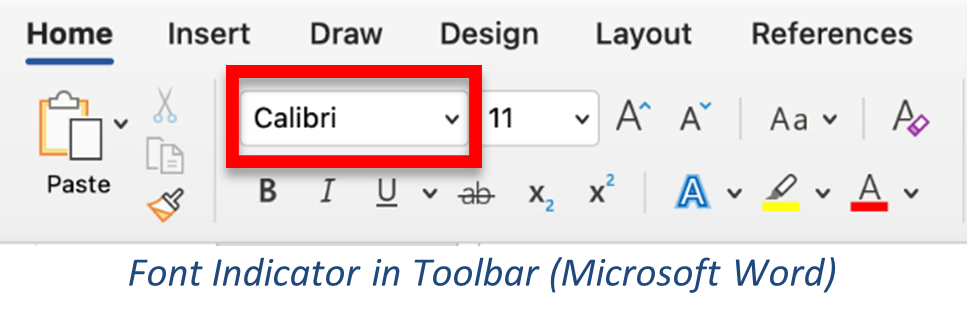
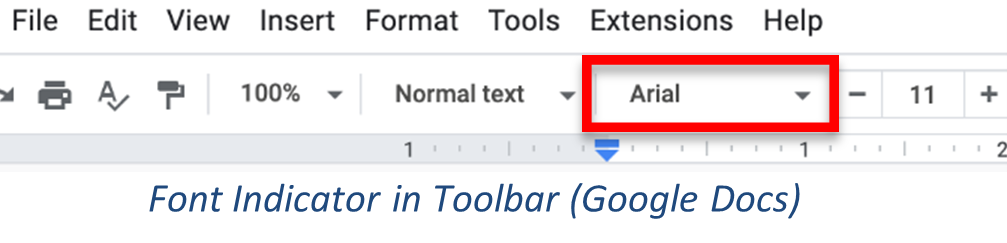
To search for a specific font, type its name in the font box. As you type, font names will autofill; when the font name you want has auto-filled, press Enter to apply that font. If you have the menu open, the font name will also be highlighted in the list.
Font size describes the size of the text and how much space it will take up on a page. Headings and subheadings are often in a larger font than the rest of the text.
To change font size:
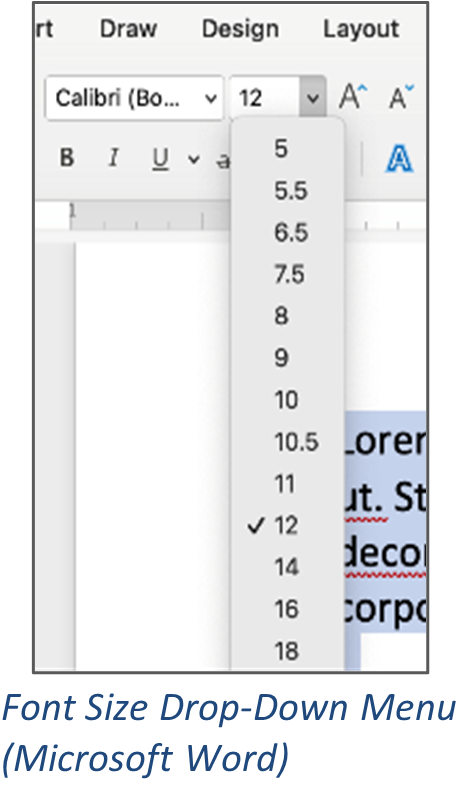
Microsoft Word and Google Docs also provide buttons to quickly increase and decrease font size. In Microsoft Word, click the bigger and smaller letter “A” buttons to the right of the font size box. In Google Docs, click the + and - symbols to either side of the font size number.
Bold, italics, and underline are common text-formatting features. The bold feature thickens the text’s individual characters, like this. Bold is often used to make paper titles, keywords, subheadings, or other pieces of text stand out and guide the readers eye. The italics feature tilts the characters of text slightly to the right, like this. Italics are often used to indicate something is a title, or to add emphasis to a word or phrase. The underline feature inserts a line under the text, like this, and can also be used to add emphasis.
To bold, italicize, or underline your text:
The text color feature changes the color of text, like this.
To change text color:
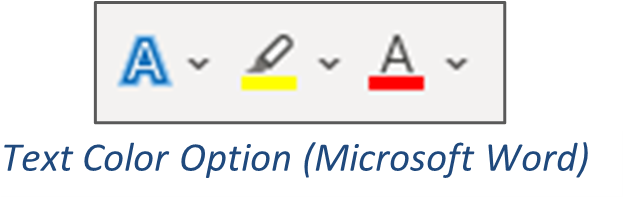
The highlight feature inserts a colored filler behind text, like this.
To highlight text:

The clear formatting feature removes all special formatting from text.
To clear formatting:

Alternatively, you can use a keyboard shortcut: